Riichi strategy: Difference between revisions
m (→Winning chance) |
m (→(Average) riichi criteria: more clarifying before riichi) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
''For strategy regarding riichi mahjong itself, see [[Strategy]]'' | ''For strategy regarding riichi mahjong itself, see [[Strategy]]'' | ||
Calling [[riichi]] comes with various considerations. While | Calling [[riichi]] comes with various considerations. While it gives a high score bonus, it also alerts players that you are in tenpai, and prevents you from [[defense|defending]]. Therefore, some discretion should be used before declaring riichi. | ||
==Assessing riichi== | == Assessing riichi == | ||
[[Image:Indefensible riichi.png|thumb|right|250px|Riichi does not let you respond to [http://tenhou.net/0/?log=2012111209gm-0009-7447-x33034e7e5279&tw=2&ts=4 any conditions that change in the future].]] <!--Aligns with the disadvantages section better here--> | |||
=== Advantages === | === Advantages === | ||
* Riichi is a [[yaku]]. It grants 1 additional han and allows any closed hand to meet the yaku requirement. | |||
* Riichi is a yaku. It grants 1 additional han and allows any closed hand to meet the yaku requirement. | |||
* You can score additional han through [[ippatsu]] and/or [[ura dora]]. In addition, you are more likely to [[tsumo]] with a riichi, increasing the chance for [[menzen tsumo]]. When considering these bonuses, a riichi is worth an average of around 1.5 han. | * You can score additional han through [[ippatsu]] and/or [[ura dora]]. In addition, you are more likely to [[tsumo]] with a riichi, increasing the chance for [[menzen tsumo]]. When considering these bonuses, a riichi is worth an average of around 1.5 han. | ||
** Each [[kan]] formed by any player provides a kan uradora to the riichi, in addition to the regular kan dora. | ** Each [[kan]] formed by any player provides a kan uradora to the riichi, in addition to the regular kan dora. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
=== Disadvantages === | === Disadvantages === | ||
* By rule, the hand is locked. | * By rule, the hand is locked. Therefore, it is impossible to change the composition of the hand in order to get a better wait or an improved score. | ||
** A riichi hand can no longer defend. If other players manage to reach tenpai, you could deal in. | ** A riichi hand can no longer defend. If other players manage to reach tenpai, you could deal in. | ||
* Riichi usually lowers the hand's win rate. A defending player is less likely to deal in, so you'll be less likely to win. | * Riichi usually lowers the hand's win rate. A defending player is less likely to deal in, so you'll be less likely to win. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
* A "riichi stick" of 1,000 points is spent to call the riichi, with the hopes of winning it back. However, other players may win the hand and capture those 1,000 points instead. | * A "riichi stick" of 1,000 points is spent to call the riichi, with the hopes of winning it back. However, other players may win the hand and capture those 1,000 points instead. | ||
== | == Alternatives == | ||
There are two main alternatives to riichi: | |||
* [[Damaten]]: entering tenpai without riichi. (Even if the hand has no yaku, any closed hand can gain yaku with [[menzen tsumo]].) | |||
* Going back to [[iishanten]]: either done to defend, or - rarely - look for upgrades (iishanten tends to allow more upgrades than tenpai). | |||
== Speed == | == Speed == | ||
[[Image:Intimidate riichi.png|thumb|right|250px|[http://tenhou.net/0/?log=2016081218gm-0029-0000-bcaa7251&tw=1&ts=14 Riichi called] to apply pressure onto the other players, with relatively low scoring differentials.]] | [[Image:Intimidate riichi.png|thumb|right|250px|[http://tenhou.net/0/?log=2016081218gm-0029-0000-bcaa7251&tw=1&ts=14 Riichi called] to apply pressure onto the other players, with relatively low scoring differentials.]] | ||
There is a big advantage to being the first to tenpai, and thus an advantage to being the first to riichi. | |||
*If an | * Only one hand can win per round. Winning first will prevent anyone else from winning. | ||
*If an opponent | * To complete a [[sequence]], a tenpai hand can call [[ron]] from anyone. Regular hands are stuck with [[chii]], which can only be called from the leftmost player. | ||
* It is difficult for opponents that aren't already in tenpai to push against a riichi: | |||
** If an opponent decides to push: progressing from [[iishanten]] to [[tenpai]] is slow. Even with great [[tile acceptance]], going iishanten -> tenpai can take a few turns - this gives you a few turns to win. | |||
** If an opponent decides to fold: great - that's one less opponent to worry about. | |||
** In a ruleset with 3 [[red five]]s, an average riichi is worth 7000 points (though this considers [[menzen tsumo]]). From an expected value standpoint, pushing an iishanten isn't wise unless the hand is very good. | |||
Due to these advantages, a | Due to these advantages, a "head start" riichi is very powerful. Even if an opponent attacks into your riichi, you have chances to win before then. Declaring riichi ''just'' for intimidation is not effective, but any sort of value can make the riichi powerful. | ||
Conversely, a chasing riichi (riichi after another player has declared riichi) is weaker for the same reasons. | Conversely, a chasing riichi (riichi after another player has declared riichi) is weaker for the same reasons. You should not shy away from a chasing riichi, though; if you reach tenpai safely, and want to attack against an opponent, you want all the value you can get. | ||
== Hand shape and waits == | == Hand shape and waits == | ||
Once a hand reaches tenpai, | Once a hand reaches tenpai, its chance of winning depends largely on its [[wait]]s. The more tiles it waits on, the better. Since most of riichi's downsides only apply if you don't win, having a good wait (2+ sided wait, >=6 tiles acceptance) makes the riichi stronger. Conversely, a bad shape riichi is less likely to win, and may want to upgrade into a better wait. | ||
[[Furiten]] weakens the hand. A furiten 2-sided wait ~= a non-furiten 1-sided wait. A furiten 3-sided wait is quite strong. | |||
== Score == | == Score == | ||
Riichi gives 1 han, and possibly more via ippatsu and ura dora. | Riichi gives 1 han, and possibly more via ippatsu and ura dora. Every han doubles score until the [[mangan]] cap, so these are all valuable. If a hand is below mangan, riichi roughly ''triples'' your average score. | ||
* | However, there are a few cases where score does not matter: | ||
*When | * Past [[mangan]], each han has reduced effectiveness. A [[haneman]]-or-higher hand shouldn't riichi because it is already very valuable, so the score bonus from riichi isn't as impactful. (For example: Going from 6 han -> 7 han doesn't increase score. 7 han -> 8 han is only a +25% boost to score.) | ||
*When | * When first with a large lead, or first during [[all last]]. In this case, damaten helps increase your win rate, allowing you to end the game faster. | ||
* When in [[all last]], where both dama and riichi will result in the same final placement (even with a direct hit riichi + 1 ura dora). | |||
That being said, the extra points from riichi often do matter. Mahjong is a game about scoring the most points, after all. | That being said, the extra points from riichi often do matter. Mahjong is a game about scoring the most points, after all. | ||
=== Winning chance === | === Winning chance === | ||
Pressing players to defend will lower your chance of winning. | Pressing players to defend will often lower your chance of winning. When a hand has a yaku other than riichi, declaring riichi generally lowers your winrate by around x70% to x80%.<ref>Miinin. ''Statistical Mahjong Strategy''.</ref> However, since riichi more-than-doubles your score (until mangan), declaring riichi offers better value under normal circumstances. If you don't care about the point boost, though, then dama is better. | ||
If you don't care about | |||
Hands which have an extremely poor wait (e.g single tile wait on dora) are so bad that riichi doesn't reduce their chance of winning by much. | Hands which have an extremely poor wait (e.g single tile wait on dora) are so bad that riichi doesn't reduce their chance of winning by much. | ||
== Point standing == | == Point standing == | ||
{{ | {{Main|Situational analysis|Kyoku}} | ||
In the first half of the game, | [[Situational analysis]] (analysis of point standings/placements/round #) is key to using riichi. In the first half of the game, the exact point standings won't be a concern. There are many opportunities to make up differences: a player who's ahead can hardly afford to rest on their laurels, while players who are behind are not as desperate. Thus, playing for expected value is strong, even with a big lead. | ||
In the latter half of the game (usually in the South round; can be earlier if a player is close to bankrupting), the point standing matters more. Most mahjong games include [[uma]], providing a huge incentive to rise/keep placements. Going from 3rd to 2nd is a major jump, and going from 3rd to 4th is a major blow. Even a +1000 point win is valuable if it causes you to rise in placement, or lets you keep your current placement. In the South round: | |||
*Players that are ahead should be more willing to dama. Late in the game, increasing your point lead doesn't matter as much, but the risk of dealing in matters more. Also, as mentioned above, dama increases your winrate, allowing you to end the game faster. | * Players that are ahead / in the lead should be more willing to dama. Late in the game, increasing your point lead doesn't matter as much, but the risk of dealing in matters more. Also, as mentioned above, dama increases your winrate, allowing you to end the game faster. | ||
* | * Players in 4th by a large amount are often forced to riichi, hoping for a big hand. | ||
* Players in the middle should analyze their own specific situations to determine if riichi is right. If being in 4th place confers a huge penalty (such as high ranked gameplay in [[tenhou.net]] and [[Majsoul]]), players not in 4th may want to dama to end the game faster, even if riichi could let them rise a place. | |||
*If a damaten win and riichi win would cause you to end up in the same placement, and it's all last, you should dama. | *If a damaten win and riichi win would cause you to end up in the same placement, and it's all last, you should dama. | ||
Overall: in the earlier end of the game, going for | Rarely, the 1000 point bet used to declare riichi can cause you to drop down a placement. If this is the case during all last, you probably shouldn't riichi if you have another yaku. | ||
Overall: in the earlier end of the game, going for expected points can be a good idea. In the later end, aiming to retain (or improve) your placement usually matters more than the points themselves. This consideration will depend on the game's [[oka and uma]] settings. | |||
== Hand lock == | == Hand lock == | ||
By declaring riichi, the hand is locked - you cannot upgrade the hand to improve the wait, gain yaku, or play | By declaring riichi, the hand is locked - you cannot upgrade the hand to improve the wait, gain yaku, or play defensively. | ||
=== Waiting for upgrades === | === Waiting for upgrades === | ||
| Line 91: | Line 90: | ||
As the round progresses, you should be more willing to riichi than to wait for an upgrade; you don't have as much time to wait for an upgrade. | As the round progresses, you should be more willing to riichi than to wait for an upgrade; you don't have as much time to wait for an upgrade. | ||
Note: when you reach tenpai but are waiting for an upgrade, it's often best to stay at [[iishanten]], ''unless'' you have an expensive hand. If you enter tenpai with a 46-pin middle [[kanchan]], you have 8 tiles worth of upgrade. If you decline tenpai, you'll often have more than 8 tiles to upgrade with. For example, if you discard 6-pin, leaving 4-pin and a 2334-man shape, you have 18 tiles worth of non-furiten uprades. | Note: when you reach tenpai but are waiting for an upgrade, it's often best to stay at [[iishanten]], ''unless'' you have an expensive hand (3+ han). If you enter tenpai with a 46-pin middle [[kanchan]], you have 8 tiles worth of upgrade. If you decline tenpai, you'll often have more than 8 tiles to upgrade with. For example, if you discard 6-pin, leaving 4-pin and a 2334-man shape, you have 18 tiles worth of non-furiten uprades. | ||
=== Defense === | === Defense === | ||
The hand lock prevents you from defending, which is the biggest risk of declaring riichi. Often, the reward is worthwhile | The hand lock prevents you from defending, which is the biggest risk of declaring riichi. Often, the reward is worthwhile: even without riichi, it is often best to keep tenpai instead of defending. But if the risk of dealing in is greater than riichi's extra value, then it can be a bigger point of concern. | ||
The most common example is when you are far in the lead, since the extra points don't matter much. It can also happen when in 2nd, it's late in the game, and 1st is too far ahead of you. | |||
== Furiten == | == Furiten == | ||
| Line 103: | Line 102: | ||
Declaring riichi means that, if the player declines the first possible ron, they enter permanent [[furiten]]. Meanwhile, if a damaten hand skips a win, it is only in furiten until the next discard. | Declaring riichi means that, if the player declines the first possible ron, they enter permanent [[furiten]]. Meanwhile, if a damaten hand skips a win, it is only in furiten until the next discard. | ||
* Damaten has better control over [[takame and yasume]]. A dama hand can choose to reject a lower-scoring tile. However, since riichi is worth 1.5 han on average, the difference between takame/yasume needs to be 3+ han in order to matter. | |||
* A damaten hand can try and target a specific player. You may want to ron to get a player below 0 points, ending the game immediately. Or you may wish to avoid calling ron on a player with 0 points, to not end the game. This can also be done to [[gyakuten|change placement]] when near all last (e.g. targeting 1st place as 2nd). However, since riichi gives a hefty point bonus, a riichi hand might improve your placement even if you tsumo or ron the "wrong" player. | |||
== Oikake riichi == | == Oikake riichi == | ||
| Line 111: | Line 109: | ||
'''Oikake riichi''' {{kana|追いかけリーチ}} is a "chasing riichi", or a declared riichi after another player had already declared riichi. In this state, two or even three players have simultaneously declared riichi. In this state, players are locked into a "riichi duel" - any riichi declarer is liable of playing into another's riichi call. | '''Oikake riichi''' {{kana|追いかけリーチ}} is a "chasing riichi", or a declared riichi after another player had already declared riichi. In this state, two or even three players have simultaneously declared riichi. In this state, players are locked into a "riichi duel" - any riichi declarer is liable of playing into another's riichi call. | ||
Players often declare chasing riichi | Players often declare chasing riichi when: | ||
* They have no option to defend. | |||
* They have a strong hand. | |||
** If tenpai happens to be reached with a good wait after an opponent's riichi, then declaring chasing riichi is strong. Your win rate far exceeds the deal-in rate. (If the hand is still iishanten when the first riichi is declared, a very strong hand is needed to "full" attack.) | |||
When you do have the option to defend, the decision to push or fold should depend more on [[shanten]], [[tile acceptance]], and wait rather than the value of the hand. | |||
If [[abortive draw]]s are enabled, the hand will end in abortive draw when all four players declare riichi (after the 4th riichi declarer discards a tile). | If [[abortive draw]]s are enabled, the hand will end in abortive draw when all four players declare riichi (after the 4th riichi declarer discards a tile). | ||
== (Average) riichi criteria == | |||
With all these factors in mind, the following is a rough guideline of when to and not to riichi. This list should be taken with a grain of salt - they may change based on the exact hand composition, your opponents hands/discards, point standings, round #, and the current turn #. | |||
'''Do riichi:''' | |||
* When first to tenpai, good wait (>= 6 tiles), 1-4 han after riichi. Even a riichi-only hand with a [[ryanmen]] wait is positive value. | |||
* When first to tenpai, bad wait, 2-4 han after riichi. A 2 han 40 fu hand (e.g. riichi tanyao) is better than damaten. | |||
* When declaring chasing riichi, with a hand worth pushing, if it's at/below mangan post riichi. | |||
Note: "First to tenpai" also assumes it is before the 3rd row of discards (turn 12 or earlier). Past turn 12, it can still be worthwhile to riichi, but beware of [[dama]]/open tenpai. | |||
'''Don't riichi:''' | |||
* With a bad wait riichi-only hand. | |||
* With a hand that's haneman or higher before riichi. | |||
* With a 4 han (before riichi) bad wait hand. | |||
** A 4 han (before riichi) good wait hand should call riichi if its early in the game, but dama when late in the game. | |||
* With an extreme amount of upgrades. The amount of upgrades need to be very high to skip tenpai. In the early game, to delay tenpai there should be: 6 types of tiles (~24 tiles total) for a wait upgrade, or 4 types (~16 tiles total) to double value. As the game proresses, an even larger # of upgrades is needed to beat riichi. | |||
* After point standing analysis. You don't need to riichi with a large lead in all last, or if dama would result in you taking 1st during all last. | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:12, 2 October 2024

For strategy regarding riichi mahjong itself, see Strategy
Calling riichi comes with various considerations. While it gives a high score bonus, it also alerts players that you are in tenpai, and prevents you from defending. Therefore, some discretion should be used before declaring riichi.
Assessing riichi
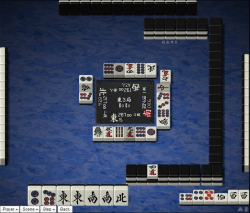
Advantages
- Riichi is a yaku. It grants 1 additional han and allows any closed hand to meet the yaku requirement.
- You can score additional han through ippatsu and/or ura dora. In addition, you are more likely to tsumo with a riichi, increasing the chance for menzen tsumo. When considering these bonuses, a riichi is worth an average of around 1.5 han.
- Each kan formed by any player provides a kan uradora to the riichi, in addition to the regular kan dora.
- Other players may defend against a riichi call, giving up their hands to avoid dealing in.
Disadvantages
- By rule, the hand is locked. Therefore, it is impossible to change the composition of the hand in order to get a better wait or an improved score.
- A riichi hand can no longer defend. If other players manage to reach tenpai, you could deal in.
- Riichi usually lowers the hand's win rate. A defending player is less likely to deal in, so you'll be less likely to win.
- If you do not declare a win on the first possible winning tile, you will enter furiten.
- A "riichi stick" of 1,000 points is spent to call the riichi, with the hopes of winning it back. However, other players may win the hand and capture those 1,000 points instead.
Alternatives
There are two main alternatives to riichi:
- Damaten: entering tenpai without riichi. (Even if the hand has no yaku, any closed hand can gain yaku with menzen tsumo.)
- Going back to iishanten: either done to defend, or - rarely - look for upgrades (iishanten tends to allow more upgrades than tenpai).
Speed
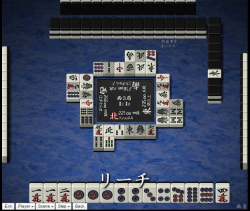
There is a big advantage to being the first to tenpai, and thus an advantage to being the first to riichi.
- Only one hand can win per round. Winning first will prevent anyone else from winning.
- To complete a sequence, a tenpai hand can call ron from anyone. Regular hands are stuck with chii, which can only be called from the leftmost player.
- It is difficult for opponents that aren't already in tenpai to push against a riichi:
- If an opponent decides to push: progressing from iishanten to tenpai is slow. Even with great tile acceptance, going iishanten -> tenpai can take a few turns - this gives you a few turns to win.
- If an opponent decides to fold: great - that's one less opponent to worry about.
- In a ruleset with 3 red fives, an average riichi is worth 7000 points (though this considers menzen tsumo). From an expected value standpoint, pushing an iishanten isn't wise unless the hand is very good.
Due to these advantages, a "head start" riichi is very powerful. Even if an opponent attacks into your riichi, you have chances to win before then. Declaring riichi just for intimidation is not effective, but any sort of value can make the riichi powerful.
Conversely, a chasing riichi (riichi after another player has declared riichi) is weaker for the same reasons. You should not shy away from a chasing riichi, though; if you reach tenpai safely, and want to attack against an opponent, you want all the value you can get.
Hand shape and waits
Once a hand reaches tenpai, its chance of winning depends largely on its waits. The more tiles it waits on, the better. Since most of riichi's downsides only apply if you don't win, having a good wait (2+ sided wait, >=6 tiles acceptance) makes the riichi stronger. Conversely, a bad shape riichi is less likely to win, and may want to upgrade into a better wait.
Furiten weakens the hand. A furiten 2-sided wait ~= a non-furiten 1-sided wait. A furiten 3-sided wait is quite strong.
Score
Riichi gives 1 han, and possibly more via ippatsu and ura dora. Every han doubles score until the mangan cap, so these are all valuable. If a hand is below mangan, riichi roughly triples your average score.
However, there are a few cases where score does not matter:
- Past mangan, each han has reduced effectiveness. A haneman-or-higher hand shouldn't riichi because it is already very valuable, so the score bonus from riichi isn't as impactful. (For example: Going from 6 han -> 7 han doesn't increase score. 7 han -> 8 han is only a +25% boost to score.)
- When first with a large lead, or first during all last. In this case, damaten helps increase your win rate, allowing you to end the game faster.
- When in all last, where both dama and riichi will result in the same final placement (even with a direct hit riichi + 1 ura dora).
That being said, the extra points from riichi often do matter. Mahjong is a game about scoring the most points, after all.
Winning chance
Pressing players to defend will often lower your chance of winning. When a hand has a yaku other than riichi, declaring riichi generally lowers your winrate by around x70% to x80%.[1] However, since riichi more-than-doubles your score (until mangan), declaring riichi offers better value under normal circumstances. If you don't care about the point boost, though, then dama is better.
Hands which have an extremely poor wait (e.g single tile wait on dora) are so bad that riichi doesn't reduce their chance of winning by much.
Point standing
Situational analysis (analysis of point standings/placements/round #) is key to using riichi. In the first half of the game, the exact point standings won't be a concern. There are many opportunities to make up differences: a player who's ahead can hardly afford to rest on their laurels, while players who are behind are not as desperate. Thus, playing for expected value is strong, even with a big lead.
In the latter half of the game (usually in the South round; can be earlier if a player is close to bankrupting), the point standing matters more. Most mahjong games include uma, providing a huge incentive to rise/keep placements. Going from 3rd to 2nd is a major jump, and going from 3rd to 4th is a major blow. Even a +1000 point win is valuable if it causes you to rise in placement, or lets you keep your current placement. In the South round:
- Players that are ahead / in the lead should be more willing to dama. Late in the game, increasing your point lead doesn't matter as much, but the risk of dealing in matters more. Also, as mentioned above, dama increases your winrate, allowing you to end the game faster.
- Players in 4th by a large amount are often forced to riichi, hoping for a big hand.
- Players in the middle should analyze their own specific situations to determine if riichi is right. If being in 4th place confers a huge penalty (such as high ranked gameplay in tenhou.net and Majsoul), players not in 4th may want to dama to end the game faster, even if riichi could let them rise a place.
- If a damaten win and riichi win would cause you to end up in the same placement, and it's all last, you should dama.
Rarely, the 1000 point bet used to declare riichi can cause you to drop down a placement. If this is the case during all last, you probably shouldn't riichi if you have another yaku.
Overall: in the earlier end of the game, going for expected points can be a good idea. In the later end, aiming to retain (or improve) your placement usually matters more than the points themselves. This consideration will depend on the game's oka and uma settings.
Hand lock
By declaring riichi, the hand is locked - you cannot upgrade the hand to improve the wait, gain yaku, or play defensively.
Waiting for upgrades
Being the first to riichi is a big advantage of itself. So, if you want to delay riichi to wait for an upgrade, you should have many tiles that you could upgrade off of. As a contrived example:
You could upgrade the hand to a two-sided or better wait with: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , which is up to 48 tiles. When considering the number of upgrades, you should consider every visible tile. You must also watch out for furiten.
, which is up to 48 tiles. When considering the number of upgrades, you should consider every visible tile. You must also watch out for furiten.
As the round progresses, you should be more willing to riichi than to wait for an upgrade; you don't have as much time to wait for an upgrade.
Note: when you reach tenpai but are waiting for an upgrade, it's often best to stay at iishanten, unless you have an expensive hand (3+ han). If you enter tenpai with a 46-pin middle kanchan, you have 8 tiles worth of upgrade. If you decline tenpai, you'll often have more than 8 tiles to upgrade with. For example, if you discard 6-pin, leaving 4-pin and a 2334-man shape, you have 18 tiles worth of non-furiten uprades.
Defense
The hand lock prevents you from defending, which is the biggest risk of declaring riichi. Often, the reward is worthwhile: even without riichi, it is often best to keep tenpai instead of defending. But if the risk of dealing in is greater than riichi's extra value, then it can be a bigger point of concern.
The most common example is when you are far in the lead, since the extra points don't matter much. It can also happen when in 2nd, it's late in the game, and 1st is too far ahead of you.
Furiten
Declaring riichi means that, if the player declines the first possible ron, they enter permanent furiten. Meanwhile, if a damaten hand skips a win, it is only in furiten until the next discard.
- Damaten has better control over takame and yasume. A dama hand can choose to reject a lower-scoring tile. However, since riichi is worth 1.5 han on average, the difference between takame/yasume needs to be 3+ han in order to matter.
- A damaten hand can try and target a specific player. You may want to ron to get a player below 0 points, ending the game immediately. Or you may wish to avoid calling ron on a player with 0 points, to not end the game. This can also be done to change placement when near all last (e.g. targeting 1st place as 2nd). However, since riichi gives a hefty point bonus, a riichi hand might improve your placement even if you tsumo or ron the "wrong" player.
Oikake riichi
Oikake riichi 「追いかけリーチ」 is a "chasing riichi", or a declared riichi after another player had already declared riichi. In this state, two or even three players have simultaneously declared riichi. In this state, players are locked into a "riichi duel" - any riichi declarer is liable of playing into another's riichi call.
Players often declare chasing riichi when:
- They have no option to defend.
- They have a strong hand.
- If tenpai happens to be reached with a good wait after an opponent's riichi, then declaring chasing riichi is strong. Your win rate far exceeds the deal-in rate. (If the hand is still iishanten when the first riichi is declared, a very strong hand is needed to "full" attack.)
When you do have the option to defend, the decision to push or fold should depend more on shanten, tile acceptance, and wait rather than the value of the hand.
If abortive draws are enabled, the hand will end in abortive draw when all four players declare riichi (after the 4th riichi declarer discards a tile).
(Average) riichi criteria
With all these factors in mind, the following is a rough guideline of when to and not to riichi. This list should be taken with a grain of salt - they may change based on the exact hand composition, your opponents hands/discards, point standings, round #, and the current turn #.
Do riichi:
- When first to tenpai, good wait (>= 6 tiles), 1-4 han after riichi. Even a riichi-only hand with a ryanmen wait is positive value.
- When first to tenpai, bad wait, 2-4 han after riichi. A 2 han 40 fu hand (e.g. riichi tanyao) is better than damaten.
- When declaring chasing riichi, with a hand worth pushing, if it's at/below mangan post riichi.
Note: "First to tenpai" also assumes it is before the 3rd row of discards (turn 12 or earlier). Past turn 12, it can still be worthwhile to riichi, but beware of dama/open tenpai.
Don't riichi:
- With a bad wait riichi-only hand.
- With a hand that's haneman or higher before riichi.
- With a 4 han (before riichi) bad wait hand.
- A 4 han (before riichi) good wait hand should call riichi if its early in the game, but dama when late in the game.
- With an extreme amount of upgrades. The amount of upgrades need to be very high to skip tenpai. In the early game, to delay tenpai there should be: 6 types of tiles (~24 tiles total) for a wait upgrade, or 4 types (~16 tiles total) to double value. As the game proresses, an even larger # of upgrades is needed to beat riichi.
- After point standing analysis. You don't need to riichi with a large lead in all last, or if dama would result in you taking 1st during all last.
References
- ↑ Miinin. Statistical Mahjong Strategy.
External links
- 【麻雀講座】ダマテンにすべき手の基準~"場況"という曖昧さを解消する (YouTube)
- Unimaru's coverage of riichi vs damaten
| |||||||||||