Riichi: Difference between revisions
m (→Double riichi) |
m (→Ippatsu) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
=== Ippatsu === | === Ippatsu === | ||
'''Ippatsu''' {{kana|一発}} is awarded if the player receives a winning tile within an uninterrupted set of | '''Ippatsu''' {{kana|一発}} is a yaku completely dependent on riichi. It is awarded if the player receives a winning tile within an uninterrupted set of opponent tile draws after the riichi declaration. The earliest possible chance to win with ippatsu comes from the shimocha's discard (player to the right). The latest possible chance to win with ippatsu is with the player's next drawn tile after the riichi declaration. In turn, this yaku may only be scored with riichi and is worth an additional 1 han, in conjunction with riichi. | ||
[[Naki|Tile calls]] may end the chance for ippatsu any time before the riichi declarer draws the next tile. Once again, in order to award ippatsu, the cycle between a player's riichi discard and next turn to discard must be uninterrupted. Thus, players may actually use the option to make tile calls to deliberately deny a player the chance for ippatsu. | [[Naki|Tile calls]] may immediately end the chance for ippatsu any time before the riichi declarer draws the next tile. This includes any calls for [[kan]], except for [[shouminkan]]. Once again, in order to award ippatsu, the cycle between a player's riichi discard and next turn to discard must be uninterrupted. Thus, players may actually use the option to make tile calls to deliberately deny a player the chance for ippatsu. | ||
Finally, by definition, ippatsu requires a riichi declaration to be in effect. Therefore, ippatsu cannot function as a stand-alone yaku. | Finally, by definition, ippatsu requires a riichi declaration to be in effect. Therefore, ippatsu cannot function as a stand-alone yaku. | ||
Revision as of 02:49, 27 July 2014
| Type | Yaku |
|---|---|
| Kanji | 立直 or リーチ |
| English | Ready hand |
| Value | 1 han (closed only) |
| Speed | Varies |
| Difficulty | At discretion |
Riichi 「立直」 or 「リーチ」 is the most commonly used yaku in the game. This yaku may apply to any closed hand and may be declared upon achieving tenpai. Due to its common usage, various specific game scenarios must be considered when using riichi.
Unlike other yaku, the call for riichi operates at a player's discretion and is certainly not mandatory. Players may simply opt not to call riichi and retain the secrecy of a hand's tenpai status, using a tactic known as damaten.
Rules
When a player has a closed tenpai hand, the player may declare riichi. Doing so gains the hand 1 han. To declare riichi, a player announces riichi and discards a tile facing sideways in the discard pile. This is done to indicate when riichi was called. If that tile is claimed by another player for an open meld, then the next discard is turned sideways as a replacement.
Unless the first sideways discard is claimed for a win immediately, the riichi announcer now places a bet of 1,000 points on the table. This bet is collected by the next player to win a hand. Of course, a player must also have 1,000 points to begin with, assuming that a game ends with negative scores. Specific rulesets may handle differently what happens to the bet on a multiple win.
After a riichi declaration, the hand remains locked and unchangeable. In this state, the player is simply waiting for a winning tile to appear, either by draw or discard. However, a notable exception may involve calls for kan.
It is not allowed to declare riichi when less than four tiles remain in the wall. The player must be able to draw one more tile in an uninterrupted set of turns. For any hand, the absolute last chance to call riichi is when the player has a chance to score riichi, haitei, ippatsu, and mentsumo.
Noten riichi
A player may actually declare riichi with a noten hand. This is a noten riichi 「ノテン立直」. This type of play is highly not advisable. If and when the hand results in ryuukyoku, then it is required of the player to reveal the hand to show tenpai. The noten riichi would naturally show noten; and it is subject to chombo. Of course, computer based play is usually programmed to prevent players from making such a riichi declaration.
Kan during riichi
When a riichi declarer holds three identical tiles and draws the fourth after the riichi announcement, he may form an ankan from these tiles instead of discarding the fourth. The hand composition and the possible winning tiles may not change: It is not allowed to declare kan if, for some possible winning tile, any of the three identical tiles may be interpreted as part of a shuntsu or part of the pair.
Example 1:
It is not allowed to kan the fours. The manzu tiles may either be interpreted as a 3-4 ryanmen wait and a 4-4 pair, or as a 4-man ankou with a 3-man tanki wait. A kan call would alter the wait just for a 3-man tanki. For a legal kan declaration, the three identical tiles would have to be an ankou in any interpretation. Had the player drawn a west wind, he would have been allowed to kan it.
Example 2:
In this example, none of the waits are affected by any of the kan possibilities. The waiting tiles are completely unrelated to any of the existing triplets in this hand. Therefore, it is acceptable to call kan during riichi here.
Furiten
During riichi, a player may be furiten. In this case, the riichi is considered to be a furiten riichi. Likewise, after calling riichi, a player may decline the option to call on a winning tile, whether it be by self-draw or by discard. However, if a win is declined, then the riichi declared hand is subject to furiten for the remainder of the hand. Thus, all tiles discarded after the riichi declaration, as indicated by the discarded sideways tile, are considered to be guaranteed safe tiles. While it is advised to declare a win on the first opportunity, some plays may require a player not to do so under very specific circumstances. Of course, such play requires caution.
Ura dora
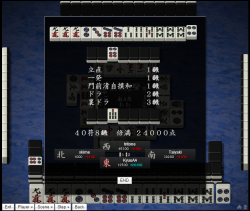
When a riichi declarer wins, he may flip the tiles underneath the dora and kan dora indicators. These flipped ura dora indicators may increase the value of his hand.
Tochuu ryuukoku
Tochuu ryuukoku, or abortive draw, is in effect when suucha riichi occurs. In this case, three riichis have been called; and a fourth one is called in place. If the discarded tile is not claimed for a win, then the hand ends.
Riichi based yaku
Two yaku are specifically associated with riichi: ippatsu and double riichi.
Ippatsu
Ippatsu 「一発」 is a yaku completely dependent on riichi. It is awarded if the player receives a winning tile within an uninterrupted set of opponent tile draws after the riichi declaration. The earliest possible chance to win with ippatsu comes from the shimocha's discard (player to the right). The latest possible chance to win with ippatsu is with the player's next drawn tile after the riichi declaration. In turn, this yaku may only be scored with riichi and is worth an additional 1 han, in conjunction with riichi.
Tile calls may immediately end the chance for ippatsu any time before the riichi declarer draws the next tile. This includes any calls for kan, except for shouminkan. Once again, in order to award ippatsu, the cycle between a player's riichi discard and next turn to discard must be uninterrupted. Thus, players may actually use the option to make tile calls to deliberately deny a player the chance for ippatsu.
Finally, by definition, ippatsu requires a riichi declaration to be in effect. Therefore, ippatsu cannot function as a stand-alone yaku.
Double riichi
Double riichi 「ダブルリーチ」 is a special case for riichi, where the player declares riichi on the first turn. No tile call may have interrupted the turn order before the declaration, where applicable. For the dealer, double riichi can never be interrupted. As the name implies, this yaku is worth 2 han instead of 1 han, as a bonus for the initial timing. With the added han value, a call for double riichi has a huge advantage over the other players in conjunction with the immediate speed and value compared to conventional riichi calls.
Compatibility
^ Ippatsu requires riichi to be of any use.
| RCH | DRI | IPP^ | SMO | TAN | PFU | IPK | ITT | YAK | SDJ | SDO | TOI | SNA | SNK | CHA | JUN | RPK | SSG | HRO | HON | CHN | CHI | RIN | HAI | HOU | CHK | |
| RCH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DRI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IPP |
Given the rules, riichi is compatible with all other yaku. Likewise, riichi and double riichi cannot be combined as they are essentially the same yaku. It just happens that double riichi is a specific instance of riichi. As for ippatsu, per rule, it is impossible to attain ippatsu without riichi.
Once again, the prospect for rinshan kaihou to work with riichi is dependent on the legality of the kan call during riichi. With computer interfaces, this rule may be enforced by disabling a player's ability to call the kan during this situation. However, with actual tiles, a player must be aware of this legality.
Strategy
Calling riichi is an optional play. Therefore, players often have to make various considerations, when it comes to using riichi. Often, this depends on the discarded tiles, how early or late in the hand, the hand value, and/or the player's hand composition. If possible, a player may opt not to use riichi at all and instead employ the strategy of damaten.
Advantages
- Any closed hand becomes eligible for winning by ron.
- Riichi is an automatic yaku and is eligible to count for 1 additional han (after a win).
- Access to the ura-dora (after a win).
- Kans formed by any player provide two extra dora indicators for the riichi declarer instead of one.
- Other players are recommended to defend against riichi calls, if possible or needed. Otherwise, players run the risk of falling to that hand.
Disadvantages
- It is less likely for opponents to deal in.
- By rule, the hand is locked. Therefore, it is impossible to change the composition of the hand in order to get a better wait or an improved score.
- Likewise, a player can no longer defend and instead wait for a winning tile.
- Other players still have the option to develop their hands and potentially "snipe" the hand. Example.
- It is highly recommended to declare the win on the first instance of a winning tile, even if the tile is a yasume or a lower scoring tile (based on yaku). Otherwise, the hand is subject to furiten. A riichi call disables a person's ability to be selective of points from particular players (if need be).
Miscellaneous considerations
Once again, riichi is a discretionary play. In fact, in all instances of considering and calling riichi, risk is involved. Therefore, various factors must be considered before employing using riichi. At the same time, many plays involving riichi are highly recommended. Employing riichi is a matter of the current game state. Now, here are some questions to consider:
- What game round is it?
- Is the lead currently held?
- Overall, what is the current point standing?
- Is it necessary to improve the hand by calling riichi?
- Would damaten be sufficient?
- Can the hand be improved by drawing particular tiles?
- How many tiles are available for winning?
- Is it safe to discard the extra tile, to call riichi?
- Is it worth calling riichi at all?
- Did anyone else call riichi previously?
- How many tile draws are left?
Oikake riichi
Oikake riichi 「追いかけリーチ」 is a declared riichi, after another player had already declared riichi. In this state, two or even three players have simultaneously declared riichi; and thus, the game becomes a contest between two or three tenpai hands. In this state, any riichi declarer is liable of playing into another's riichi call.
The process of four active riichi hands is not possible due to suucha riichi, or four called riichi. In this case, the hand ends if the fourth riichi discard is not a winning tile for any of the previous three.
External links
- Riichi in Japanese Wikipedia
- Ippatsu in Japanese Wikipedia.
- Double riichi in Japanese Wikipedia.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
